Restrict Sensitive Data



Avoid Simple Passwords

Avoid Suspicious Downloads

Keep Software Updated

Always Enable Antivirus

Be Cautious with Attachments

Restrict Sensitive Data
Use a Firewall

Backup Your Files

Enable Two-Factor Authentication

Have a Response Plan

Passwords are often the first and sometimes the only line of defense in digital security. In many cases, users opt for convenience over security and choose simple, easily guessable passwords such as "123456", "password", or even parts of their names. These simple choices provide little to no protection against cyber threats.

When attackers use automated tools to try out common passwords, they can gain access to accounts in minutes. The consequences of a breach include stolen personal information, unauthorized transactions, and further intrusion into connected systems. Simple passwords are a weak link in your overall security strategy.

To improve your security, always create strong, unique passwords. A robust password should include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Additionally, consider using a reliable password manager that can generate complex passwords and store them securely, so you don’t have to remember each one.

The internet offers a wealth of resources, but not all downloads are safe. Many websites lure users with enticing offers, only to distribute software bundled with malware. Suspicious downloads often masquerade as legitimate applications or files.

Downloading files from unverified sources can introduce harmful viruses and malware into your system. Once infected, your computer could be used to steal sensitive information, monitor your online activities, or even join a botnet that participates in large-scale cyber attacks.

Always download files only from reputable sources and official websites. Check reviews and user feedback if you’re unsure about a download’s legitimacy. Additionally, run a virus scan on any file before opening it to ensure it is safe.

Software updates aren’t just about new features—they’re crucial for security. Every update often includes patches that fix vulnerabilities and bugs discovered in previous versions, ensuring that your software remains resilient against new types of attacks.

Outdated software can be a treasure trove for hackers. Vulnerabilities left unpatched provide an easy entry point for cybercriminals. Without updates, your system remains exposed to known exploits that have long been remedied in newer versions.

Enable automatic updates on your devices and applications whenever possible. Regularly check for patches, not just for your operating system, but also for your antivirus and other critical software to ensure you’re protected from the latest threats.

Antivirus software acts as a shield between your device and potential threats. It continuously scans for malware and other malicious activities, alerting you to any risks before they escalate into serious problems.

Disabling your antivirus or neglecting to update it can leave your system open to infections. Without this layer of protection, viruses, ransomware, and other malware can easily slip through, leading to data theft or system damage.

Always keep your antivirus software enabled and updated. Run regular scans to detect any hidden threats early, and consider using additional security tools for layered protection.

Email remains one of the most popular communication tools—and unfortunately, also one of the most common ways for malware to spread. Attachments from unknown senders can often hide dangerous payloads.

Opening an attachment without verifying its source can result in an immediate infection. Cybercriminals frequently use this method to distribute ransomware or spyware, putting both personal and professional data at risk.

Always be cautious with email attachments. Verify the sender’s identity before opening files, and when in doubt, scan the attachment with your antivirus software or simply contact the sender to confirm its legitimacy.

Sensitive data, ranging from personal records to corporate secrets, requires the utmost protection. The more widely accessible this information is, the higher the risk it faces from unauthorized parties.
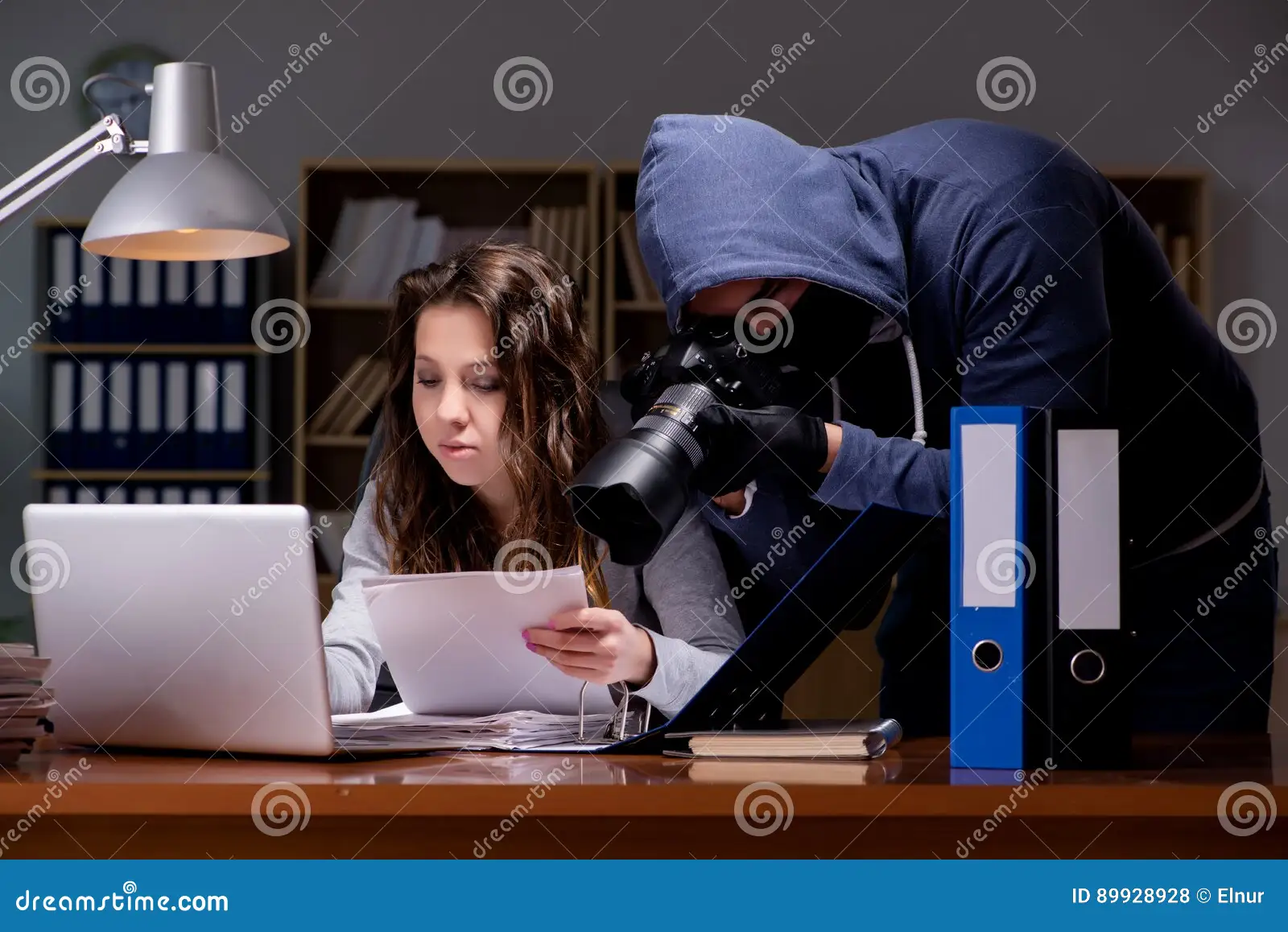

If sensitive data is not properly restricted, it can lead to devastating data breaches. Unauthorized access can result in financial loss, legal consequences, and severe damage to personal or organizational reputations.

Implement strict access controls and ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data. Use encryption for data both in transit and at rest, and perform regular audits of access permissions to keep your data secure.

A firewall acts as a barrier that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. It is one of the key components of network security.
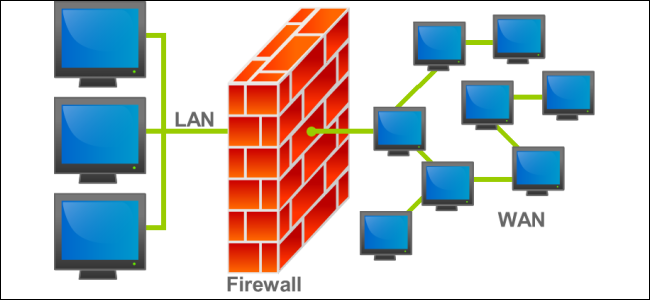
Without a properly configured firewall, your system is exposed to unfiltered internet traffic. This vulnerability can allow hackers to bypass other security measures and access your network remotely.

Install a firewall and ensure it is correctly configured to block unauthorized traffic. Regularly update its settings and combine both hardware and software firewalls for a more robust defense.

Backing up your files is an essential part of any cybersecurity strategy. Regular backups ensure that your important data remains accessible even if your primary device is compromised.

If your device is compromised by ransomware, hardware failure, or accidental deletion, the absence of a backup can lead to permanent data loss, severely impacting personal or business operations.
Develop a regular backup strategy using external drives or secure cloud storage. Automate the backup process when possible and test recovery procedures periodically to ensure your backups are reliable.

Two-factor authentication (2FA) provides an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification in addition to your password. This additional step makes it much more difficult for attackers to compromise your accounts.

Even strong passwords can be compromised through phishing, data breaches, or keylogging. Without a second factor, attackers only need one piece of information to gain access to your sensitive accounts.
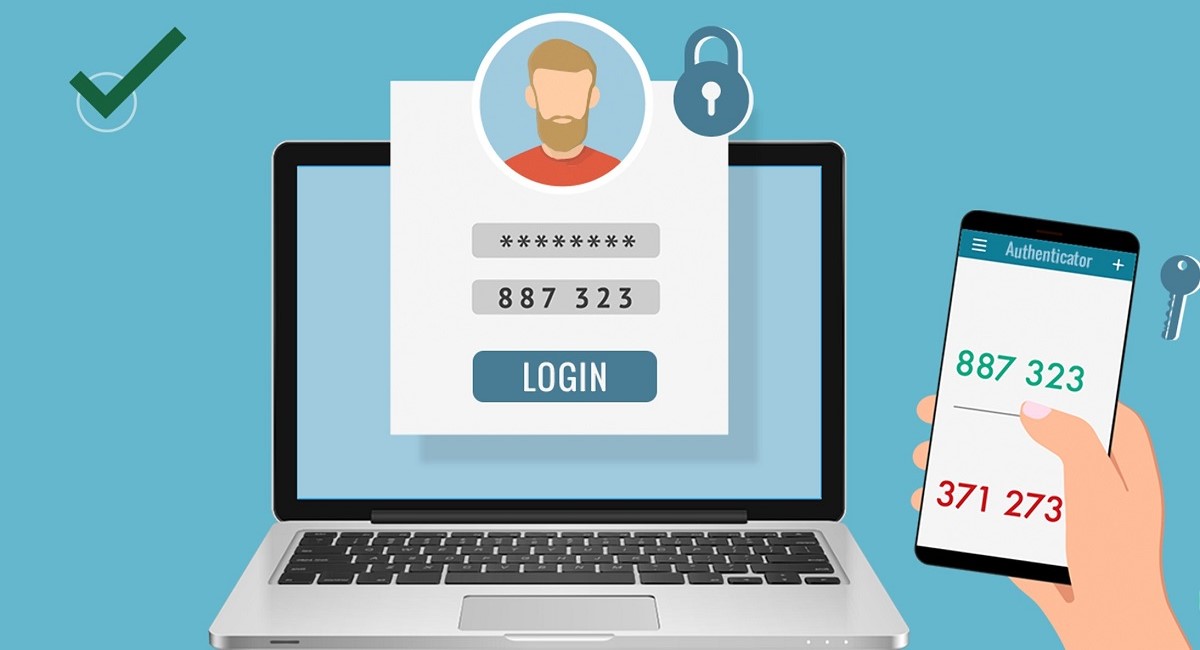

Enable 2FA on every account that supports it, using an authenticator app or hardware token for the most secure method. This greatly reduces the risk of unauthorized access even if your password is compromised.

No system is completely immune to cyber attacks, which makes having an incident response plan essential. A comprehensive response plan outlines the procedures and responsibilities needed to quickly contain and remediate a breach.

Without a clear response plan, organizations and individuals may experience prolonged downtime, significant data loss, and greater overall damage when a breach occurs. Uncertainty during a crisis can lead to delays and mistakes.

Develop and document a detailed incident response plan that includes containment, investigation, and recovery procedures. Regularly review and test the plan to ensure everyone involved understands their role, minimizing the impact of any future incidents.